Curriculum
An example of a food web
Look at the simple food web below. It shows the many ways that living things in an area depend on other living things for food. Examine it closely.
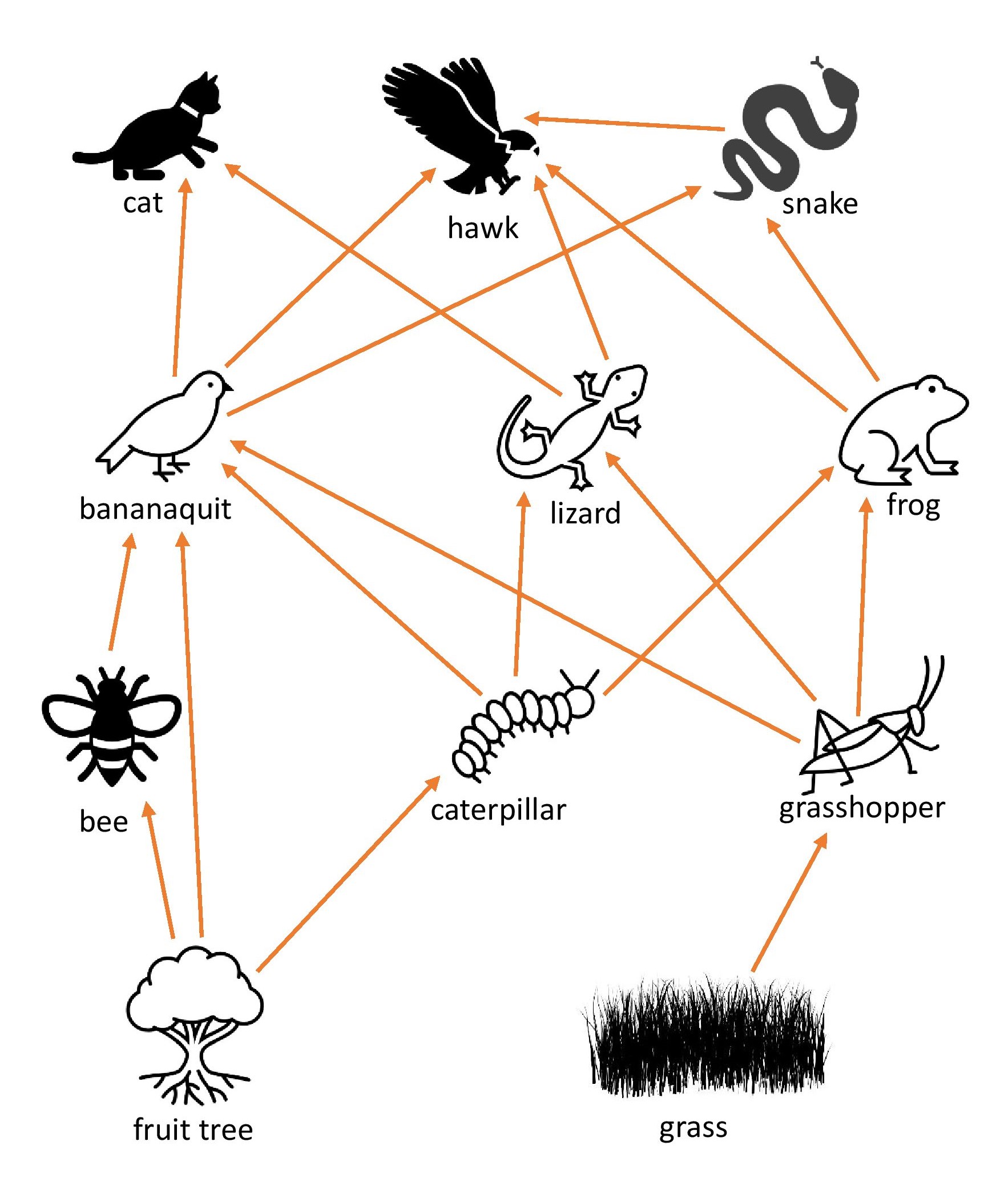
There are different types of living things in this ecosystem. Some of them include:
Producers: Some living things like plants and algae produce their own food. Therefore they are called producers. The producers in this ecosystem are grass and fruit trees.
Note: Algae are living things which can produce their own food. They are not plants as they do not have leaves, stems or roots.
Primary Consumers: Animals that eat plants are called primary consumers. They are also called herbivores. In the food web above, grasshoppers eat the grass and caterpillars eat the leaves of the fruit trees. Grasshoppers and caterpillars are primary consumers in our food web. Can you name another primary consumer in the food web above?
Secondary Consumers: Animals that eat primary consumers are called secondary consumers. They are also called carnivores because they eat other animals. In the food web above we can see that lizards are secondary consumers as they eat grasshoppers and caterpillars. Can you see any other secondary consumers in the food web above?
Some animals eat both plants and animals. They are called omnivores. In the food web above we can see that the bananquit eats grasshoppers, bees and caterpillars. However it also eats fruit from the fruit trees. Therefore it is an omnivore.
Many connected food chains
Food webs are made up of many connected food chains. If you look closely at the food web above, you will be able to pick out several food chains such as:
-
grass → grasshopper→ lizard→ cat
-
grass → grasshopper→ frog → snake → hawk
-
fruit tree → bee → bananaquit → cat
Can you see any more food chains in the food web above?